News & Events
Straight Line Depreciation Calculator
- April 10, 2024
- Posted by: maile
- Category: Bookkeeping

From time to time, I will invite other voices to weigh in on important issues in EdTech. We hope to provide a well-rounded, multi-faceted look at the past, present, the future of EdTech in the US and internationally. In regression analysis, the difference between the observed value of the dependent variable and the predicted value is called the residual. Let’s say the company assumes each vehicle will have a salvage value of $5,000.
How often should I update my salvage value estimate?
Constant use and other factors like the nature and quality of these assets cause a continual deterioration. Consider the depreciation rate, which is the percentage of the asset’s value that is lost each year. Next, the annual depreciation can be calculated by subtracting the residual value from the PP&E purchase price and dividing that amount by the useful life assumption. Furthermore, salvage value also aids in strategic decision-making related to the potential sale of depreciated assets for parts.
Market Demand
Click “Calculate Salvage Value” to see the estimated salvage value based on straight-line depreciation.3. Use the eBay market check feature to compare your estimate with current market prices.4. Incorporating a robust ERP system like Deskera can significantly enhance how businesses manage and calculate salvage value.
FAQ about Calculating Salvage Value
- In this fashion, it prepares you to understand the true cost of using an asset over time.
- To make an informed choice, you need to calculate the after-tax salvage value of the equipment, which will significantly impact your company’s financial statements and tax liabilities.
- As a general rule, the longer the useful life or lease period of an asset, the lower its residual value.
- Otherwise, you’d be “double-dipping” on your tax deductions, according to the IRS.
- Resale value is a similar concept, but it refers to a car that has been purchased, rather than leased.
In 1998, the company restated its earnings by $1.7 billion – the largest restatement in history. Other commonly used names for salvage value are “disposal value,” “residual value,” and “scrap value.” Net salvage value is salvage value minus any removal costs. Though residual value is an important part in preparing a company’s financial statements, residual value is often not directly shown on the reports. In accounting, owner’s equity is the residual net assets after the deduction of liabilities.
This provides a true reflection of the asset’s value and helps in presenting a more accurate financial position of the company. It is is an essential component of financial accounting, allowing businesses to allocate the cost of an asset over its useful life. One method of determining depreciation involves considering the asset’s salvage value. The salvage value is the estimated residual value of the asset at the end of its useful life. The after-tax salvage value is the net value of an asset after it has been sold and all related taxes have been deducted.
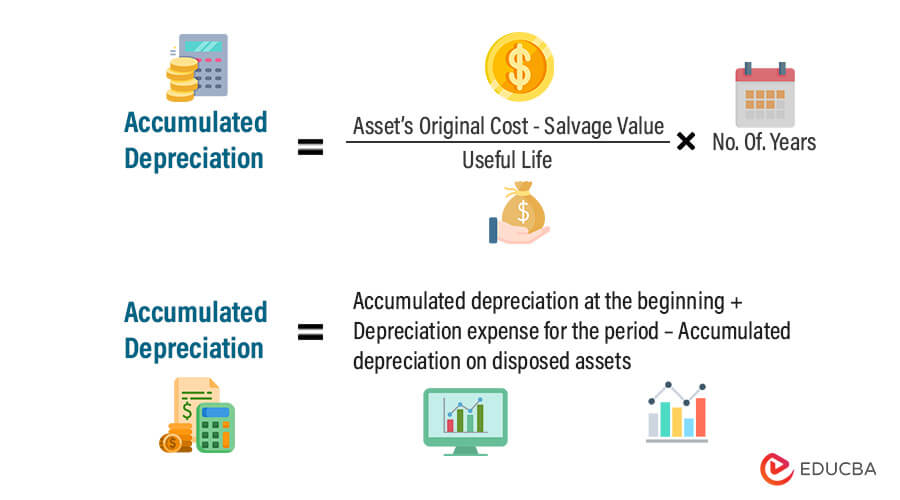
An asset’s depreciable amount is its total accumulated depreciation after all depreciation expense has been recorded, which is also the result of historical cost minus salvage value. The carrying value of an asset as it is being depreciated is its historical cost minus accumulated depreciation to date. Moreover, for businesses and individuals alike, knowing the salvage value is vital for financial planning, mainly while calculating depreciation expenses or determining tax benefits. To calculate the annual depreciation expense, the depreciable cost (i.e. the asset’s purchase price minus the residual value assumption) is divided by the useful life assumption. The straight-line method is suitable for assets that are expected to provide equal benefit over their useful life, such as buildings or vehicles. The units of production method is appropriate for assets that are mainly used based on its output or production levels, such as machinery.
All users have to do is to input the asset’s initial cost, useful life, and depreciation rate, and thus they can find its salvage value. In this way, it makes things easier to plan for replacements or evaluate resale opportunities. A Salvage Value Calculator is reasonably useful for finding out the remaining worth of an asset at the end of its useful life. Salvage value, often called residual value, allows businesses and individuals to project the potential resale or scrap worth of assets like vehicles, equipment, or buildings. The depreciation rate is influenced by the asset’s useful life, salvage value, and the method of depreciation chosen, such as the straight-line or double-declining balance method.
The declining balance method is best suited for assets that are expected to be more productive in their early years and less productive as time goes on. The sum-of-the-years’ digits method is generally used for assets with a higher productivity pattern in the early years and slower tulsa tax law attorney productivity in later years. Companies estimate salvage value to determine the amount to which an asset’s value is depreciated over its useful life. By subtracting the salvage value from the original cost, companies can calculate the carrying value of the asset after depreciation.
This means that of the $250,000 the company paid, the company expects to recover $40,000 at the end of the useful life. Now, you are ready to record a depreciation journal entry towards the end of the accounting period. We can see this example to calculate salvage value and record depreciation in accounts.
Investors can use after-tax salvage value calculations to assess the profitability of investments and the potential return on asset sales. The condition of the asset is an essential factor in determining its salvage value. An asset in good condition is likely to have a higher salvage value compared to one that is damaged or in poor condition. The better the condition, the more valuable the asset is likely to be in the salvage market. The straight line calculation, as the name suggests, is a straight line drop in asset value. CFI is the global institution behind the financial modeling and valuation analyst FMVA® Designation.
